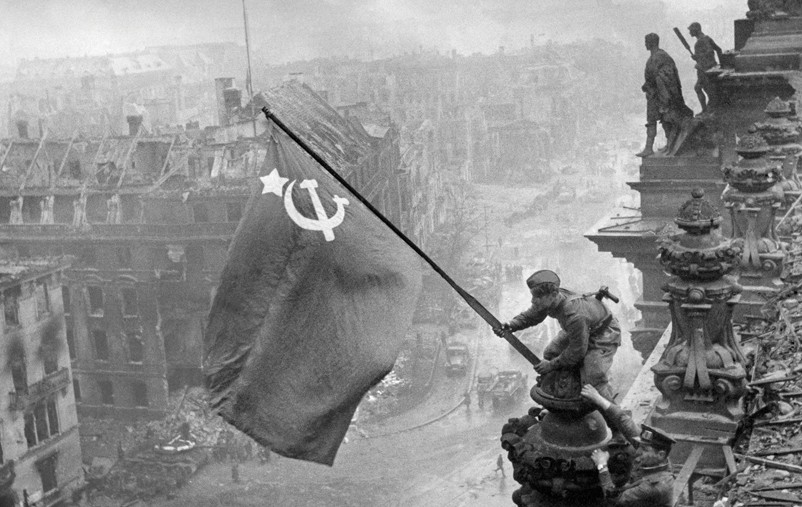
War photography holds immense sway in shaping public perceptions and political decision-making during military conflicts, employing various methods and techniques. It realistically portrays events and scenes in conflict zones, conveying the destruction, human losses, and humanitarian suffering directly, thus directing public attention to the magnitude of the disaster and the difficult humanitarian situation.
War photographs also evoke emotions in the audience, such as anger, sadness, and compassion, enabling the shaping of public opinion and increasing solidarity with the victims, supporting humanitarian intervention or changes in foreign policy. Additionally, they may expose the negative aspects of conflict and military escalation.
On the other hand, governments and armies often use war photos to influence public opinion and justify their political and military decisions, by focusing on the positive aspects of military efforts and highlighting humanitarian or strategic objectives.
War images generally play a significant role in shaping public opinion and political decisions during military conflicts, therefore, they require careful handling and awareness by the media, politicians, and the international community.
Moreover, photographs are extensively used as a means to document events, crimes, and human rights violations in conflict areas, providing strong evidence of the facts and visually proving the events and crimes, making them a valuable tool for journalists, human rights organisations, and witnesses in documenting what occurs.
They can also help raise public awareness about events in conflict areas, becoming part of the historical record that enables people worldwide to understand the situation and work towards solutions.
Furthermore, photographs can push the international community towards taking action.
When the world sees the pain and suffering depicted in war photos, it increases the pressure on governments and international organisations to intervene or impose sanctions, especially when such photos are considered testimonies of individuals who witnessed or suffered from crimes and violations enabling the use of these testimonies in investigations and trials to confirm events.
However, photographs must be handled with care and integrity, as they can be forged or inaccurately used at times. Therefore, documenting the source and verifying the accuracy of images before using them in legal or political contexts is crucial.

War Photography and the Power of Laws and Ethics
War photography raises numerous ethical and legal issues due to the difficult conditions under which photography is conducted in conflict zones and the impact of images on individuals and audiences. Capturing images of individuals in conflict zones can violate their privacy and dignity.
Thus, war photographers and journalists must fully respect the rights of individuals and avoid capturing images that could be misused for defamation or espionage. In some cases, individuals’ consent must be obtained before publishing their images, especially if these images depict their faces or identifiable details.
Moreover, photography in conflict zones serves as a powerful means to document crimes and violations. However, this photography must be based on high ethical standards, and the evidence must be presented in a way that respects the rights of victims and suspects. Sharing images requires consent from the photographer and consideration of the rights of individuals depicted in the images, whether on social media or in the media, with full respect for privacy rights.
Animated Graphics Simulating Cyber and Hybrid Wars
Graphic design and animation can effectively highlight the challenges of modern warfare, such as cybercrimes and hybrid wars, as well as explain complex concepts in an easily understandable manner for the public, illustrating how cyber-attacks or hybrid strategies work.
They can also highlight the human impacts of modern wars, such as the impact on civilians’ daily lives and humanitarian violations, fostering engagement with modern warfare issues.
Accordingly, maps can be drawn to illustrate cyber-attack activities or the effects of hybrid wars on national security to raise public awareness of the importance of addressing modern security challenges and encourage viewers to participate and think about these issues. Additionally, they can direct attention to the state’s policy in confronting modern security challenges and clarifying the plans and strategies adopted.
However, it is important to carefully and accurately design these graphics and animations to ensure the accuracy of information and positive impact on the audience.
Moreover, ethical and legal considerations regarding copyright and data privacy rights must be taken into account when using these tools.
Analytical Imaging and Artificial Intelligence: Zooming in on Conflict Areas
Analytical imaging and artificial intelligence (AI) are powerful tools used to analyse geographic images and provide intelligence about conflict zones. Such tools are used to examine geographic images and identify terrains, environmental patterns, and human activity in conflict zones in addition to monitoring changes over time, in military movements, destruction, and human activities.
Moreover, AI-based tools can analyse geographical images and extract patterns and intelligence information, such as potential forces and suspicious activities.
Furthermore, analyzing movement and behaviour can also help identify unauthorised activities.
Using deep learning and image recognition techniques, such tools can classify potential targets in geographic images, identify military facilities, and determine types of weapons and equipment.
All of this is done by processing spatial information to obtain accurate details about locations and surrounding areas, enabling the identification of strategic locations, routes, and deployment patterns, and contributing to the generation of accurate reports and analyses based on data extracted from images.
Additionally, any interested party can use historical data and AI analytics to predict potential activities in conflict areas, which contributes to the process of strategic planning.
However, it is crucial to emphasize the significance of security and privacy when collecting and processing geographic and aerial images, as well as compliance with relevant national and international laws.

The Impact of Photography on Raising Awareness and Promoting Relief Efforts
Photographs have a significant impact on raising awareness of the situations of refugees and conflict-affected individuals and enhancing relief efforts. They reflect the reality of life for those affected by conflicts, refugees, and migrants.
These photos can be used to document the difficult conditions experienced by these individuals, including the lack of shelter, food, and healthcare services.
Moreover, they can be used to spread a message of sympathy and solidarity with these individuals, encouraging donations and participation in relief efforts. Humanitarian organizations and international entities can use them to shed light on the essential needs of the affected and refugees, emphasizing the need to provide shelter, clean water, food, and healthcare services.
In this context, photos can influence decision-makers and governments, encouraging them to take humanitarian action. When the public and leaders see images depicting difficult situations, pressure can increase to contribute to solutions and support relief efforts.
Additionally, they can help promote transparency and accountability for humanitarian organizations and governments, and they can be used to monitor aid delivery and ensure its effective distribution to those in need.
Symbolism in War Photography
War photography strategically employs images to create symbols representing specific communities and audiences, which can significantly influence public perception and political decisions.
This Symbolism can be used to represent nationalism and national identity. For instance, photos showing national flags or soldiers can be used to enhance the unity and solidarity of the people in the face of military challenges.
Additionally, individuals or groups can be depicted as icons of resistance or resilience against external attacks, becoming symbols representing resilience and strength in facing waves of distortion and foreign propaganda.
In terms of security, images can be used to create negative symbolism for hostile groups and terrorist organisations, affecting public perceptions and increasing resistance to terrorist propaganda.
Therefore, military and war images should be carefully analysed to understand their symbolism and potential impact on the audience and political decisions.
Moreover, ethical, cultural, and political contexts must be considered when interpreting and understanding these symbols.
The War Photographer: Humanity Before the Image
The impact of war photography on photographers working in conflict areas can be harsh psychologically and emotionally. Studies show that they witness horrific scenes and violence, which can leave deep psychological scars, such as psychological shock and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) due to their experiences.
War photographers face increasing psychological pressure and high levels of anxiety and depression due to repeated exposure to difficult and tragic situations.
Working in conflict areas leads to continuous stress due to harsh conditions and constant danger. This stress can lead to moral and physical fatigue, making it difficult for them to reintegrate into communities after their return.
In such cases, photographers may experience social isolation and difficulty understanding people who have not experienced similar experiences.
Moreover, this line of work affects their personal relationships as they are usually preoccupied with work as well as constantly being exposed to violence and tragedy, which negatively affects their family and social relationships.
They may sometimes find it difficult to deal with difficult memories and shocking images they have witnessed. These memories can continue to affect their mental state long after their mission ends.
To help war photographers deal with these challenges they must be provided with psychological and social support and assistance. Media, humanitarian organizations, and governments must also establish policies and procedures to protect the health of photographers and ensure they receive the necessary support.

Forgery in War Photography and the Credibility of Images
Verifying the accuracy and credibility of images in war photography is a serious challenge, as images can be manipulated or forged in the context of conflicts. Ways to verify the accuracy of images include:
1. Source Verification: The first step in verifying the accuracy of images is to identify their source. Was the image captured by a trusted photographer, or was it circulated from an unknown source? Attempt to verify the identity of the photographer and the date the image was taken.
2. Visual Credibility: The image itself can be analyzed to look for any evidence of forgery, such as differences in lighting or excessive modifications to the image. Additionally, you can verify the consistency of objects and people in the image with the alleged time and place.
3. Searching For Evidence: You can search for evidence of authenticity within the image, such as the presence of geographical landmarks or recognizable facial features. Additionally, you can compare the image with other sources to verify the consistency of events and information.
4. Consulting Experts: You may need to consult experts in digital analysis and photography to assist in verifying the images. They can provide advanced analysis of the images to detect any signs of forgery.
5. Reviewing Reliable Sources: Review reputable media sources and newspapers that publish the images and verify the date and credibility of these sources. If the images are published in trusted media, this increases the likelihood of their accuracy.
6. Collaborating with Independent Media Organizations: Collaborate with independent media organizations and human rights organizations to verify the accuracy of images and information in conflict areas.
7. Utilizing Modern Technologies: Technologies such as digital data analysis and artificial intelligence can help verify the accuracy of images and detect manipulation.
Verifying the accuracy of images in conflict areas is critical to making the correct political and humanitarian decisions and avoiding relying on misleading or forged information.
How Will Photography and Image Transmission Methods Change in the Future of Wars and Conflicts?
War photography technology will continue to evolve, leading to changes in photography and image transmission methods during wars and conflicts. Here are some expected developments and how this industry might change in the future:
1. Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (Drones): The use of drones in collecting data and images in conflict areas will continue, with improvements in drone technologies such as high-resolution imaging and increased flight range and speed, allowing access to hard-to-reach areas and accurate event documentation.
2. 3D Imaging: Three-dimensional imaging may be used to create three-dimensional models of conflict areas and potential targets, helping to analyze data more deeply and provide more accurate details.
3. Artificial Intelligence and Data Analysis: Improvements in deep learning and data analysis techniques will enhance our ability to analyze and understand images faster and more accurately. Artificial intelligence will be used to filter and classify images and analyze geographical information better.
4. Wireless Networks and Data Transmission: High-speed wireless communication networks will be available in more areas, making it easier to transmit images and data quickly to main databases for rapid analysis.
5. Encryption and Security: Security will play a crucial role in transmitting war images and data. Improvements in encryption techniques will protect data from hacking and manipulation.
6. Real-Time and Live Streaming: Technology will enable the transmission of images and data in real time, allowing for instant monitoring of events on the ground and quick decision-making.
7. Virtual Reality: Virtual reality and similar technologies may be used to document and analyze situations and events more clearly and in more detail.
In general, with the advancement of technology, there will be greater opportunities to improve the quality and speed of image collection and transmission in conflict areas. However, these technologies must be used safely, ethically, and in accordance with international laws and human rights.
» By: Dr Faisal Farhi (Professor and Researcher)