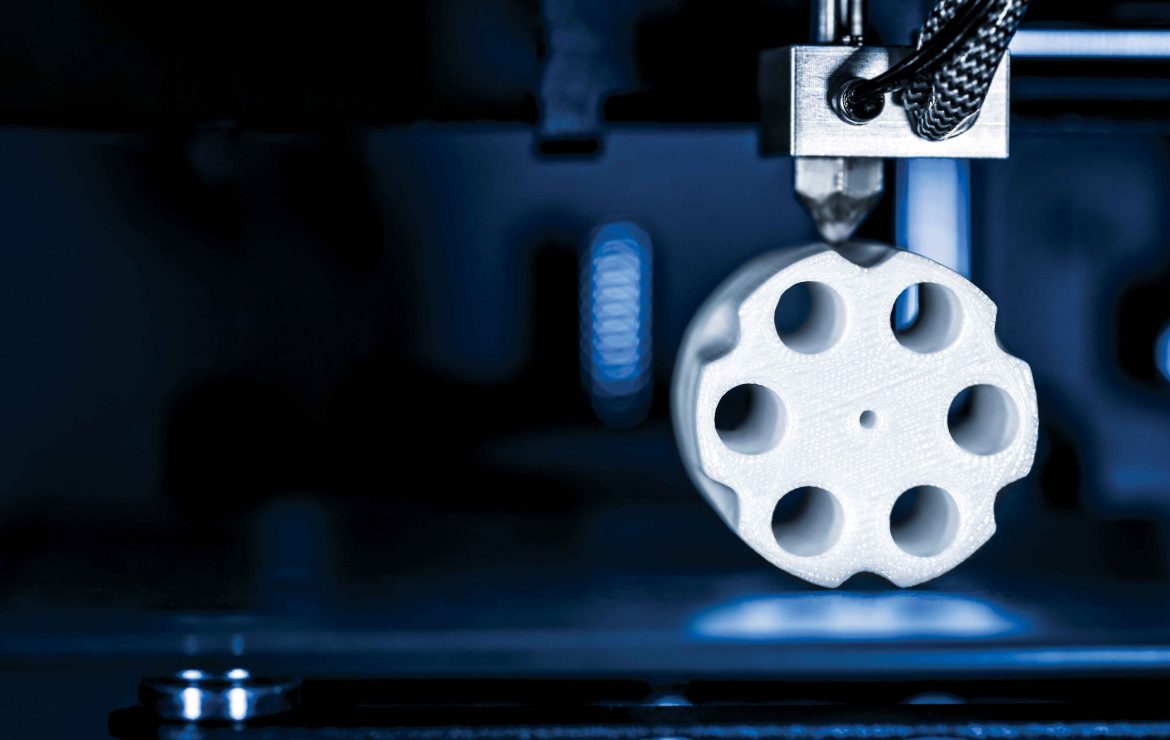
The largest armies in the world have pumped hundreds of millions of dollars into research and development in the field of 3D printing, in order to enhance the use of this technology in military manufacturing operations, and to make use of the many advantages that this new technology provides to armies.
3D printing is an additive manufacturing technique, in which a physical object is created by depositing thin layers of materials, such as metal alloys, or types of plastics and polymers, on top of each other, based on a numerical description of the product design. This technology differs from traditional removal manufacturing, which creates products by removing materials through drilling, or turning, from a solid material.
The history of 3D printing technology dates back to the early eighties of the twentieth century, and developed slowly until ten years ago, as it was subject to the intellectual property laws of 3D Systems and its founder, Chuck Hill, who invented this technology.
With the lifting of the ban, technology began to witness rapid development, especially with regard to the development of printing machines at a lower cost. In the past five years only, the cost of printers has changed. After the price of the printer exceeded 50 thousand US dollars, its price is now only 1800 dollars. Get it for under $500.
There has also been an expansion in the areas of their use, such as medicine, alternative prosthetic devices, simulating ancient statues, consumer and household products, and even the construction of walls of houses and ships, as well as some military uses.

3D military manufacturing
This technology has begun to be used in military manufacturing, but to a limited extent so far. 3D printers are used in the production of fighter engines, as well as spare parts for some weapons, such as tanks and submarines. Many countries of the world, especially the armies of major countries, are aware of the benefits of 3D manufacturing. Therefore, they tended to develop national strategies to coordinate efforts to benefit from this new technology.
The U.S. military began expanding the use of 3D printing, and the DoD’s Joint Defense Manufacturing Council intervened earlier in 2021 to coordinate it all under a unified strategy to employ additive manufacturing to enhance military readiness, reduce costs, shorten supply chains, and accelerate innovation. The Pentagon’s first additive manufacturing strategy calls for the integration of 3D printing into the defense industrial base and its employment in all branches of the armed forces.
The US military is currently reviewing parts of weapon systems to see which parts can be remanufactured using 3D printing, especially those found in older systems, such as the B-52 strategic bomber. The benefits of 3D manufacturing can be explained as follows:
1 Reduce costs and increase performance: The US Army wants to 3D-print one-piece combat vehicle hulls. The US military contracted with the non-profit ASTRO America for research and development in April 2021 to oversee the development of the world’s largest 3D metal printer to manufacture one-piece structures, which in the end will cost less, weigh less, and will be faster in production, and most importantly, it will be more resilient to various shocks and attacks, especially as better designs are developed for it.
One-piece combat vehicles are nothing new, as they have been produced in the past and have proven to be extremely durable even at a reduced weight. The challenge was to expand its production at the time, which was related to the fact that its production using traditional methods of manufacturing was very expensive, and it was difficult to produce it on a large scale.
With the advent of additive manufacturing, and the launch of the US Army’s “Jointless hull” program, the problem of large-scale production of US combat vehicles can be solved in the near future. The success of the 3D manufacturing system in the production of one-piece vehicles will increase the vehicles’ ability to withstand the damage of impacts even with reduced weight and cost.
2 Saving time: A 3D printer can be used to construct entire buildings with quick-drying concrete in just 36 hours. The US Marines used a 3D printer from the manufacturer Icon to build a reinforced concrete structure, wide enough to conceal a truck-mounted multiple missile- launching system.
Similarly, it took the US Air Force about 16 weeks to produce a spare part for the F-16 fighter, but using the additive printing technology, the required part was produced in just two weeks. It also usually takes about 5 months to build a small submarine. Now, thanks to 3D printing, it can be built in just 4 weeks. On July 24, 2020, the US Navy unveiled the first 3D-printed submarine hull for the US Army.
3 The production of old spare parts: The 3D printer can be used to produce spare parts for old vehicles and aircraft, which have been discontinued by the manufacturer. In order to produce these spare parts, large sums of money, which may reach thousands of dollars, are required. And with a 3D printer, the cost of producing it is falling dramatically.
An example of this is the US Army’s printing of spare parts for the 41-year-old Black Hawk helicopter, and the B-2 Spirit bomber, as the US Department of Defense intends to keep these machines in service for, at least, another decad, so it switched to 3D printing to manufacture parts. The same method is also being used with the American B-52 bomber.
4 Production of Unique Components: Industry experts agree that 3D printing has changed the limitations that were imposed on innovative designs, as the potential of new designs generated by 3D printers is much higher than that of traditional manufacturing. This is because metal printing enables the creation of shapes that traditional metal fabrication processes cannot match. Even existing parts that require the joining of disparate parts can be made as a single piece using 3D printing.
The latest 3D printing technology enables the innovative production of components for a wide range of military equipment that cannot be manufactured by using traditional manufacturing methods. An example of this is General Dynamics’ fuel nozzle, where the company created a one-piece printed fuel nozzle, eliminating all internal welds that were causing problems such as fuel leaks. The result was the production of a complex fuel nozzle, which no conventional manufacturing method can produce.
5 Manufacturing sustainable components: The US Air Force has 3D-printed a new piece of titanium for the F-22 Raptor stealth fighter, and the Pentagon hopes that this is just the beginning, and that the production of additional equipment will be expanded in the same way.
It is noted that the new printed component is a fairly small part, used in the cockpit, was originally made of aluminum, and is often replaced in 80% of cases during maintenance. Unlike the aluminum part, the titanium imprinted part won’t corrode and can last through the remaining operational life of the stealth fighter, which offers a huge advantage. The US military plans, in the event of the completion of tests of the new piece, that the production of other equipment from the stealth fighter will be expanded using the same method.
6 Enhancing local manufacturing: The United States relied on purchasing personal protective equipment from China, which dominated the process of exporting it globally, but with the spread of 3D printing technology in the defense industry, this matter may contribute to the re-production and manufacture of many military components in the United States again, which was previously considered too expensive to produce, thanks to 3D printers.
7 The speed of response to any sudden developments: “Additional manufacturing” can contribute to the rapid production of any equipment or spare parts, especially if the production line has been subjected to a sudden stop due to any unexpected developments, such as the exposure of the producing factory to an attack, or the suspension of importing this component from abroad for any reason.

Additive Printing deficiencies:
Despite the previous benefits that armies can achieve from employing 3D printing in manufacturing, they still suffer from major shortcomings, and they also increase the threats facing countries. These shortcomings and threats can be detailed in the following points:
1 The difficulty of producing some military components: It is noted that some printed materials manufactured by using 3D printers sometimes do not fit the heat levels required for Ministry of Defense applications, so they cannot be used in all military manufacturing processes, and therefore there is still a need to wait for technological development in 3D printers, which allow the production of components that withstand high levels of heat.
2 Cyber intrusion: The 3D printing process needs printers connected to an Internet- connected network, or even an internal network, which exposes it to electronic(cyber) threats. It is possible that these networks will be compromised by cyber-attacks that are difficult to detect, which can affect the process of designing the 3D parts, so it is necessary that we secure such networks and avoid any security vulnerabilities.
This penetration may result in changing some designs, albeit to a limited extent, which will result in the production of military equipment such as planes or tanks, that suffer from shortcomings, or defects, which may result in their physical destruction, not to mention the possibility that the produced military designs could be stolen.
3 Managing Complex Designs: DARPA’s TRADES Transformational Design program aims to develop the math and computational tools needed to create and manage the complex design needed by 3D printers. It is expected that TRADEZ’s ultimate technologies will allow designers to more easily navigate the design space to discover innovative, complex yet achievable designs that take full advantage of new materials and advanced manufacturing methods, ultimately offering a way forward for future design systems and processes.
4 Threat of terrorist groups: Terrorists may steal designs for the production of some weapons, produce them through 3D printers, and use them to carry out terrorist operations. For example, there are fears that terrorists will steal designs to produce suicide drones and use them to threaten human life and attack critical infrastructure, in a worst-case scenario.
Although there have been concerns about 3D-printing handguns, especially after tens of thousands of people have downloaded files of parts designs for various rifles and pistols. Researchers at the American RAND Corporation concluded that it is unlikely that printed weapons would pose a new threat, as pistols produced in this manner suffer from some shortcomings in their design, which makes their performance unreliable. On the other hand, it is not difficult or costly for a person to purchase a professional rifle, illegally.
In conclusion, it can be said that “additive manufacturing” is one of the developments in military manufacturing. Despite the aforementioned challenges, it is expected that technological development will lead to overcoming them, in a way that increases military industry dependence on this technology in the future, especially with the benefits it offers.
By Dr. Shadi Mohamed